Introduction
In 2024, the blockchain industry witnessed losses exceeding $4.1 billion due to security vulnerabilities and governance failures. This staggering figure highlights not only the technological challenges surrounding blockchain implementations but also the critical need for effective governance frameworks. As the cryptocurrency ecosystem evolves, understanding blockchain governance models comparison becomes essential for developers, investors, and users alike. This article aims to dissect various governance models, their strengths and weaknesses, and their implications for blockchain networks.
What is Blockchain Governance?
Blockchain governance refers to the processes and mechanisms that influence how decisions are made within a blockchain network. Governance is crucial as it determines how protocols are upgraded, how disputes are resolved, and how stakeholders interact with the network. It comprises both on-chain governance (rules encoded into the protocol) and off-chain governance (community-based decision-making). In Vietnam, an emerging market for cryptocurrencies, understanding governance dynamics can greatly affect user trust and adoption rates.
Types of Blockchain Governance Models
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): These are fully decentralized entities run by smart contracts, where the community participates in governance decisions through token voting.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): In this model, token holders elect delegates who make decisions on behalf of the network, balancing decentralization with efficiency.
- On-Chain Governance: This model allows for formal voting mechanisms integrated directly into the blockchain protocol, where changes require consensus from stakeholders.
- Off-Chain Governance: Decisions are made by community consensus and discussions outside the blockchain, often documented through proposals and forums.
Making Sense of Governance Mechanisms
Effective governance mechanisms are vital for ensuring that a blockchain remains functional and relevant. Here are some critical aspects to consider when comparing governance models:
Consensus Mechanism Vulnerabilities
Every governance model comes with its own vulnerabilities related to consensus mechanisms. Some major drawbacks include:
- DAOs: Can be susceptible to manipulation if voting power is concentrated among large token holders.
- DPoS: Though efficient, it could lead to centralization, as delegates may act in their interests rather than those of the community.
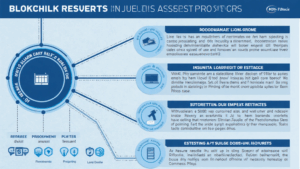
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Blockchain Governance
To gain further insights, let’s examine how different governance models have been implemented in the real world.
Ethereum‘s On-Chain Governance
Ethereum employs a somewhat hybrid approach with its on-chain governance implemented through Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs). These proposals must gain community consensus before being accepted. Ethereum‘s governance model has facilitated major upgrades, including the transition to Ethereum 2.0, enhancing scalability and security.
Tezos and its Self-Amending Protocol
Tezos utilizes a unique self-amending governance model allowing stakeholders to propose and vote on changes directly within the blockchain. This has allowed Tezos to evolve without hard forks, promoting stability and community trust.
Pros and Cons of Different Models
DAOs
- Pros: High level of decentralization; community empowerment.
- Cons: Potential for short-term decision-making; risk of large holders influencing votes.
DPoS
- Pros: Faster decision-making; increased efficiency.
- Cons: Risk of centralization; possible disconnect between delegates and the community.
On-Chain Governance
- Pros: Clarity in the process; proposed changes are easily tracked.
- Cons: Potentially slow decision-making due to the voting process.
Off-Chain Governance
- Pros: Informal debates and discussions can lead to better solutions; community engagement.
- Cons: Lack of formal accountability; decisions may not be binding.
Local Insight: The Vietnamese Market
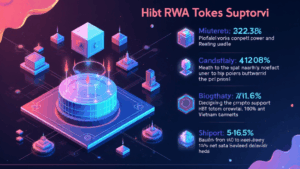
According to recent studies, the number of cryptocurrency users in Vietnam has grown by an impressive 200% in the last year. With an increasing desire for secure and decentralized financial services, understanding the local governance landscape can significantly influence community trust in blockchain solutions. Issues like tiêu chuẩn an ninh blockchain are at the forefront of discussions among investors and developers, reflecting the community’s concerns about security and ethical governance.
Future Trends in Blockchain Governance
As the blockchain ecosystem continues to innovate, several trends are likely to shape governance models moving forward:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence: AI could streamline decision-making processes within governance frameworks, enhancing efficiency while reducing risks.
- Enhanced Transparency Measures: Blockchain-based systems may introduce more robust methods of tracking governance-related transactions.
- Regulatory Influence: As governments begin to implement regulations surrounding digital assets, governance models may need to evolve to remain compliant.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the variety of blockchain governance models comparison is crucial for stakeholders within the cryptocurrency domain. With a rich mix of on-chain and off-chain methods, each model presents unique pros and cons that influence community engagement and protocol upgrades. As we move towards 2025, it’s essential for blockchain communities—especially in emerging markets like Vietnam—to adapt their governance structures to not only enhance efficiency but also to ensure security and trust in their systems. For further information on crypto governance, consider visiting hibt.com for comprehensive resources.
By Dr. Richard Liu, a blockchain expert with over 15 published papers in the field and previously led smart contract audits for prominent projects such as ChainSafe and OpenZeppelin.