Understanding Ethereum Gas Fees
With the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), Ethereum‘s network has witnessed unprecedented growth. In 2024 alone, users faced a staggering $4.1 billion loss due to DeFi hacks. Amidst this volatility, understanding Ethereum gas fees has become crucial for any cryptocurrency investor.
Gas fees refer to the charges paid to miners to validate transactions on the Ethereum blockchain. The fee is influenced by network congestion, complexity, and the urgency of the transaction. As more users join the Ethereum platform, the question arises: How do gas fees affect not just investors worldwide but specifically in emerging markets like Vietnam? Let’s break it down.
1. The Mechanics Behind Gas Fees
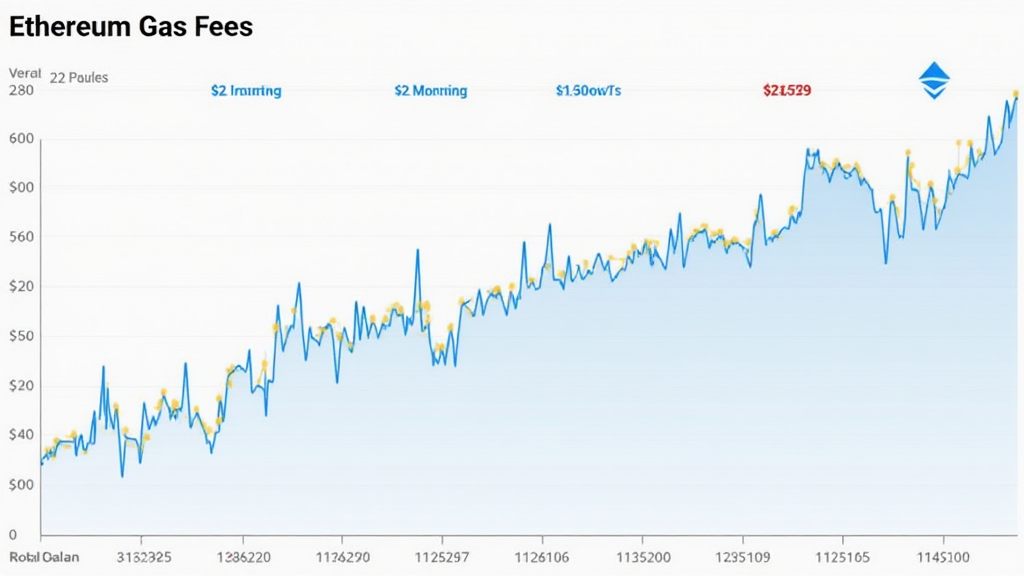
Gas fees are not fixed; they vary based on the demand and supply dynamics of the Ethereum network. During peak times, gas fees can skyrocket, making it costly for users to perform transactions. For instance, in 2023, the average gas fee reached $44 during peak hours. Users can optimize their transactions by estimating the average gas price and setting their preferences through wallets.
2. Factors Influencing Gas Fees
- Network Congestion: When many users attempt to make transactions simultaneously, fees increase.
- Complexity of Transactions: Smart contracts require more computational power, increasing fees.
- Time Sensitivity: Users willing to pay more can have their transactions prioritized.
For example, in April 2024, a major NFT drop led to gas fees exceeding $100 for a single transaction. Such fluctuations pose unique challenges for users in Vietnam, where the crypto community is rapidly expanding.
3. Impact on Vietnamese Cryptocurrency Users
According to recent statistics, the number of cryptocurrency users in Vietnam has grown by over 60% in the last year. However, the volatility of gas fees presents a significant obstacle. Users in Vietnam often engage in smaller transactions, and high fees can deter them from participating fully in the market.
Furthermore, as a significant portion of the Vietnamese population remains unbanked, the accessibility provided by cryptocurrency is vital for financial inclusion. Solutions to manage gas fees effectively could transform the landscape.
4. Solutions to Manage Gas Fees
Adapting to fluctuating gas fees is essential for users. Here are a few strategies:
- Use Layer 2 Solutions: Platforms like Polygon and Optimistic Ethereum aim to reduce gas fees significantly by processing transactions off-chain.
- Timing Transactions: Execute transactions during non-peak hours to save on gas costs.
- Optimizing Gas Settings: Use tools like gas trackers to find optimal times for transactions.
As more users adopt these strategies, they can ensure that the opportunities in the crypto space are not limited by financial barriers.
5. The Future of Ethereum and Gas Fees
Looking ahead, developments in the Ethereum network, such as the anticipated transition to Ethereum 2.0, promise to reduce congestion and optimize efficiency. This shift aims to secure the vitality of the Ethereum network, ensuring gas fees become more manageable. However, whether these advancements will fully resolve the issues remains to be seen.
As we approach 2025, additional technologies may emerge that tackle gas fee fluctuations, allowing cryptocurrency to be more accessible to users worldwide, including in Vietnam.
Conclusion
Understanding Ethereum gas fees is essential for optimizing transactions in a rapidly evolving space. As the Vietnamese cryptocurrency community grows, tackling the challenges posed by these fees will enhance user participation. Strategies such as using layer 2 solutions and timing transactions wisely can empower users to navigate fee fluctuations effectively. The future remains promising as Ethereum continues to develop.
For more resources and insights into navigating challenges in cryptocurrency, visit bitcoincashblender, your trusted platform for crypto transactions.